What is an Electric Vehicle?
An Electric Vehicle (EV) is a type of vehicle that runs on electricity instead of traditional gasoline or diesel. These vehicles use electric motors powered by batteries or fuel cells. EVs are becoming more popular due to their eco-friendly nature, as they produce fewer emissions compared to conventional cars.
What is the Full Form of EV?
The full form of EV is Electric Vehicle.
Who Invented the Electric Vehicle?
The history of electric vehicles dates back to the early 19th century. The first crude electric carriage was developed by Robert Anderson in the 1830s. However, the first practical electric vehicle was created in the late 1800s by William Morrison, an American inventor. His six-passenger electric wagon could drive at speeds of up to 14 miles per hour.
Which Battery is Used in EV?
Most modern electric vehicles use Lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are lightweight, have a high energy density, and can be recharged multiple times. They are commonly used due to their efficiency and longer lifespan compared to other battery types like lead-acid or nickel-cadmium.
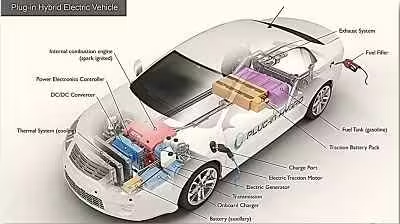
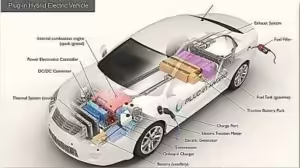
Types of Electric Vehicles
There are several types of electric vehicles based on their technology:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV): These run entirely on electric power. They need to be recharged by plugging into an external power source.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV): These combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor. They can run on both electricity and gasoline.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV): These use both an electric motor and a gasoline engine, but the battery is charged by the engine and through regenerative braking, not by plugging in.
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV): These use hydrogen as fuel, which generates electricity to power the vehicle’s motor.
Where Was the First Electric Car Made?
The first electric cars were built in Scotland and the United States in the 1830s and 1890s, respectively. Robert Anderson, from Scotland, built a non-rechargeable electric carriage, while William Morrison from the United States created the first practical, rechargeable electric vehicle.
What Was the First Electric Car?
The first practical electric car was Morrison’s electric carriage, built in the 1890s. It used non-rechargeable batteries, and though not very efficient by today’s standards, it paved the way for future developments in electric mobility.
Are EV Motors AC or DC?
Electric motors used in vehicles can be AC (Alternating Current) or DC (Direct Current). However, AC motors are more common in modern electric vehicles because they are more efficient, provide better speed control, and are easier to maintain. Most EVs use AC induction motors or permanent magnet motors.
What is the Fastest Electric Car?
As of recent records, the Rimac Nevera is the fastest electric car. It can reach speeds of 258 mph (415 km/h) and accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in just 1.85 seconds. Electric cars are known for their quick acceleration due to the instant torque generated by electric motors.
What Are the Advantages of Electric Vehicles?
Electric vehicles offer several advantages:
- Eco-friendly: EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, helping reduce air pollution.
- Energy Efficient: Electric cars are more efficient than gasoline cars. They convert around 60% of electrical energy from the grid to power the wheels.
- Lower Operating Costs: Electricity is cheaper than gasoline, and EVs require less maintenance since they have fewer moving parts.
- Quiet and Smooth: Electric motors are quieter and provide a smoother driving experience.
- Government Incentives: Many governments offer incentives such as tax credits and rebates to encourage the use of electric vehicles.
What is the Physics of Electric Cars?
Electric cars are powered by electric motors, which convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. When the driver presses the accelerator, electricity flows from the battery to the motor. This causes the rotor inside the motor to spin, generating torque that drives the wheels. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors deliver instant torque, which is why electric cars have quick acceleration.
How Do All-Electric Cars Work?
All-electric cars (Battery Electric Vehicles or BEVs) work by using electricity stored in batteries to power an electric motor. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how they work:
- Charging the Battery: The vehicle’s battery is charged using electricity from a charging station or a standard power outlet.
- Powering the Motor: When the car is turned on, electricity flows from the battery to the electric motor. The motor converts this electrical energy into mechanical energy to turn the wheels.
- Driving: When you press the accelerator, the controller sends electrical signals to the motor. The motor increases its speed, propelling the car forward.
- Regenerative Braking: EVs have a feature called regenerative braking, which allows the electric motor to act as a generator when slowing down. This helps recharge the battery by converting some of the vehicle’s kinetic energy back into electrical energy.
Conclusion
Electric vehicles are transforming the automotive industry by providing a cleaner, more efficient alternative to traditional gasoline cars. With advancements in technology, EVs are becoming faster, more affordable, and offer significant benefits, from reducing emissions to lowering maintenance costs. Whether it’s the evolution of electric motors or the types of batteries used, EVs continue to pave the way for a sustainable future.